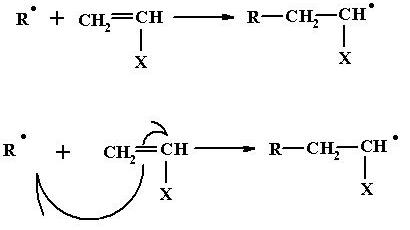
Initiation
Free radical containing unpaired electron is highly reactive and can attack any molecule which either has a lone pair of electron or is prepared to part with one of its electrons. The free radical attacks the double bond in the monomer molecule, resulting in the following chemical change.
The free radical site is now shifted from the initiator fragment to the monomer unit. This process is accompanied with an energy release of some 20 kilocalories. The free radical attack on the monomer initiating polymerization is an exothermic process, whereas free radical formation by initiator decomposition is an endothermic process.
This whole sequence in which, one free radical attacks a monomer molecule adds the monomer molecule to itself, and while so adding, simultaneously transfers that free radical site from itself to the monomer unit, is termed the initiation step.